Introduction
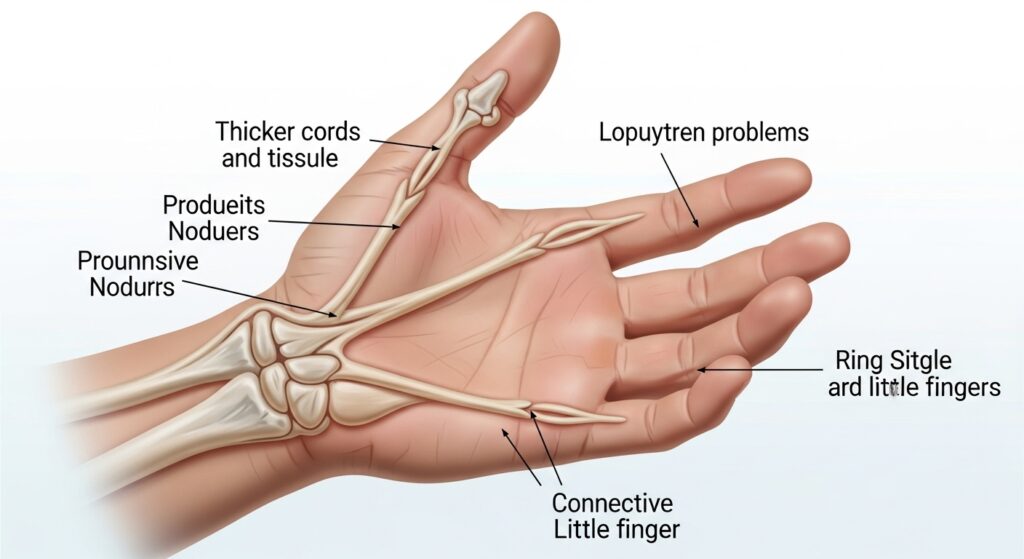
Loguytren problems, often referring to Dupuytren’s contracture or related connective tissue disorders, are conditions that affect the hand’s flexibility and function. These problems occur when the tissue beneath the skin of the palm thickens and tightens over time, pulling one or more fingers into a bent position. While loguytren problems may begin as harmless lumps or nodules in the palm, they can gradually develop into severe deformities that limit a person’s ability to grasp objects or perform everyday tasks. This condition most commonly affects men over the age of 50, though it can appear in both genders and across various age groups.
Understanding the nature of loguytren problems is crucial because early intervention can significantly improve outcomes. The condition tends to progress slowly, often without pain, leading many to ignore the early signs. However, once the fingers begin to curl, reversing the deformity becomes more difficult without medical treatment. In this article, we’ll explore what causes loguytren problems, how to recognize their symptoms, available treatment options, and ways to manage the condition effectively. Whether you’re experiencing symptoms yourself or researching for someone else, this guide will help you understand the complexities of loguytren problems and how to deal with them confidently.
What Causes Loguytren Problems?
The exact cause of loguytren problems remains unclear, but researchers believe a combination of genetic and environmental factors plays a role. A family history of the condition is one of the most significant risk factors—individuals with relatives who have loguytren problems are more likely to develop it themselves. Certain lifestyle habits, such as excessive alcohol consumption and smoking, may also contribute by affecting blood circulation and tissue health. Additionally, people with conditions like diabetes or epilepsy appear to have an increased risk of developing these connective tissue issues due to changes in collagen metabolism and nerve function.
In many cases, micro-injuries to the hand can trigger the onset of loguytren problems, especially when combined with a genetic predisposition. Some studies suggest that repetitive strain from manual labor or vibration-heavy work accelerates the thickening of the palmar fascia. The disease’s progression is unpredictable—while some experience slow development over decades, others may notice rapid worsening within months. Understanding these causes is essential to adopting preventive habits and recognizing early warning signs before significant impairment occurs.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Loguytren Problems
Early signs of loguytren problems usually appear as small, firm lumps or cords beneath the skin of the palm. These nodules may feel tender at first but typically become painless over time. As the condition progresses, the tissue thickens, forming fibrous cords that gradually pull one or more fingers toward the palm. The ring and little fingers are most commonly affected, and once the fingers begin to contract, straightening them without assistance becomes increasingly difficult.
Patients often report difficulty performing tasks such as shaking hands, wearing gloves, or placing their hands flat on a table. Unlike arthritis or tendon injuries, loguytren problems do not usually cause swelling or inflammation. Because the condition is progressive, it’s important to seek medical advice as soon as symptoms appear. Early diagnosis allows doctors to suggest minimally invasive treatments before significant contractures develop. Recognizing symptoms early is key to maintaining mobility and preventing long-term complications.
Diagnosis and Assessment
Diagnosing loguytren problems is primarily based on physical examination. Doctors assess the appearance and feel of the hand, checking for nodules and cords beneath the skin. They may perform the “tabletop test,” asking the patient to place their hand flat on a surface; inability to do so indicates a contracture. No specific blood tests or imaging are required for diagnosis, but ultrasound or MRI may be used to assess tissue thickness or rule out other conditions affecting hand function.
Assessment also involves determining the severity and progression of the disease. Physicians often classify loguytren problems into stages, ranging from mild skin changes to advanced finger deformities. This classification helps guide treatment decisions. For mild cases, observation and physical therapy might be sufficient, while severe contractures often require surgical intervention. Early and accurate assessment provides a roadmap for managing symptoms effectively and preserving hand functionality for as long as possible.
Treatment Options for Loguytren Problems
Treatment for loguytren problems depends on the stage of the disease. In early stages, non-surgical options such as corticosteroid injections, enzyme therapy (like collagenase injections), or needle aponeurotomy may help break down the cords and restore flexibility. These procedures are typically performed under local anesthesia and involve minimal recovery time. Patients are often encouraged to follow up with physical therapy to maintain hand mobility and prevent recurrence.
In more advanced cases, surgical treatment becomes necessary. A procedure known as fasciectomy involves removing or releasing the thickened tissue that causes finger bending. While surgery offers a longer-lasting solution, it also carries risks such as infection, stiffness, or recurrence. Therefore, doctors weigh the benefits and drawbacks carefully before recommending surgery. Post-surgical rehabilitation, including stretching exercises and splinting, plays a vital role in achieving the best possible recovery outcomes.
Managing Life with Loguytren Problems
Living with loguytren problems can be challenging, but adopting proactive habits can make a significant difference. Regular stretching exercises, gentle hand massages, and the use of ergonomic tools can help slow progression. Physical and occupational therapy sessions also play a key role in maintaining hand strength and flexibility. Patients are advised to avoid activities that strain the hand excessively, such as heavy gripping or vibration-intensive work.
Emotional adjustment is another vital aspect of management. Because the condition can affect daily function, it may lead to frustration or self-consciousness. Support groups and counseling can help patients cope with these feelings. Staying informed about the latest treatment advancements empowers individuals to take charge of their condition and seek professional help when necessary. Living with loguytren problems is about adapting while maintaining independence and confidence.
Prevention and Lifestyle Tips
Although there is no guaranteed way to prevent loguytren problems, adopting healthy lifestyle habits can reduce risk factors. Maintaining balanced nutrition rich in collagen-supporting nutrients, such as vitamin C and zinc, helps promote tissue health. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake are equally important, as both habits negatively affect blood flow and connective tissue repair. For individuals with diabetes, controlling blood sugar levels can also play a preventative role.
Regular hand care and awareness of early symptoms are key. People who work with their hands should take frequent breaks, use protective gloves, and perform stretching exercises to maintain flexibility. Early consultation with a healthcare professional at the first sign of nodules or stiffness can lead to better long-term outcomes. Prevention, when combined with proactive management, forms the strongest defense against progressive loguytren problems.
Conclusion
Loguytren problems are more than just a cosmetic issue—they represent a chronic condition that can significantly impact hand function and quality of life. While the exact cause remains elusive, understanding risk factors, recognizing early symptoms, and pursuing timely treatment are essential steps toward control. Modern therapies, from enzyme injections to surgical options, provide hope for those affected. However, the journey doesn’t end with treatment; ongoing care, lifestyle adjustments, and awareness are crucial for preventing recurrence.
If you suspect you’re developing loguytren problems, consult a qualified healthcare professional promptly. Early intervention can preserve mobility, reduce discomfort, and help maintain independence in daily life. With the right knowledge and proactive approach, living well with loguytren problems is entirely achievable.